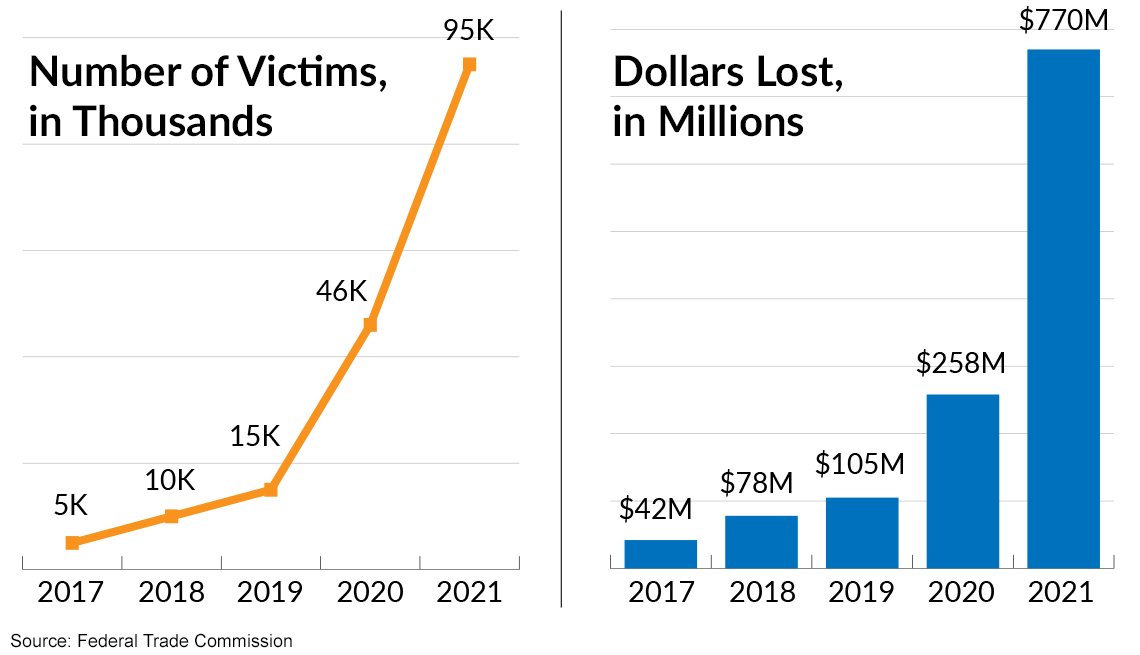
An exploit for a Windows local privilege elevation vulnerability that allows anyone to gain admin privileges in Windows 10 has been publicly disclosed by a security researcher. Threat actors who had access to a compromised device could elevate their privileges to spread laterally within the network, create new administrative users, or perform privileged commands.
What is an LPE bug?
Local privilege escalation happens when one user acquires the system rights of another user. Network intruders have different techniques for increasing privileges once they have gained access to a system. The initial intrusion could start from anywhere. Say a guest account or a local user who has carelessly written a username and password on a Post It note. Regular users typically operate at a relatively low privilege level –usually to prevent someone who obtains their credentials from gaining control of the system. Once inside, the intruder employs privilege escalation techniques to increase the level of control over the system
A windows zero-day vulnerability exploited since mid-2020

Microsoft previously said that a high-severity Windows zero-day vulnerability patched during the February 2021 Patch Tuesday was exploited in the wild since at least the summer of 2020 according to its telemetry data. The actively exploited zero-day bug was tracked as ‘CVE-2021-1732 – Windows Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability.’ As part of the January 2022 Patch Tuesday, Microsoft fixed a ‘Win32k Elevation of Privilege’ vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-21882, which is a bypass for the previously patched and actively exploited CVE-2021-1732 bug.
It was first disclosed by RyeLv, a security researcher, who explained, “The attacker can call the relevant GUI API at the user_mode to make the kernel call like xxxMenuWindowProc, xxxSBWndProc, xxxSwitchWndProc, xxxTooltipWndProc, etc. These kernel functions will trigger a callback xxxClientAllocWindowClassExtraBytes. An attacker can intercept this callback through hook xxxClientAllocWindowClassExtraBytes in KernelCallbackTable, and use the NtUserConsoleControl method to set the ConsoleWindow flag of the tagWND object, which will modify the window type”
The bug was being exploited by sophisticated groups as a zero-day issue, Microsoft said.
Microsoft’s diminishing bug-bounty rewards
This same vulnerability was apparently discovered about two years ago by an Israeli security researcher who is also the CEO of Piiano, Gil Dabah, who tweeted that he decided not to report the bug two years ago as Microsoft’s bug-bounty rewards were reduced.
Also, RyeLv stated in his technical write up for the CVE-2022-21882 vulnerability, “Improve the kernel 0day bounty, let more security researchers participate in the bounty program, and help the system to be more perfect,”
General precautions
Microsoft improving its bug bounty rewards could potentially lead to more bug reports by motivated researchers.
Many users chose to skip January 2022 updates due to the significant number of critical bugs introduced by the January 2022 updates, including reboots, L2TP VPN problems, inaccessible ReFS volumes, and Hyper-V issues during the installation of these updates. Keeping auto-updates off and researching the latest updates before installing it might be the best course of action until Microsoft updates are deemed reliable.
Sources: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/recently-fixed-windows-zero-day-actively-exploited-since-mid-2020/
https://threatpost.com/public-exploit-windows-10-bug/178135/
https://googleprojectzero.github.io/0days-in-the-wild/0day-RCAs/2022/CVE-2022-21882.html