
Security has become a crucial part of the digital era and organizations are moving towards advanced techniques to keep their networks secure from malicious threats. With new advancements in security technology, there is always a level of uncertainty about its efficacy and whether there exist loopholes in its design for exploitation. Authentication mechanisms using single or multiple factors, such as password protection, certificate validation, and bio metrics, are still vulnerable when they are static. Contextual knowledge, an essential aspect of adaptive authentication, plays a key role to dynamically validate users while minimizing risk in real time. In this way, adaptive authentication is an ideal solution for modern network security. Although many organizations are quite skeptical about this innovative technology, numerous examples, theoretical systems, industrial systems, and academic surveys shed light on the benefits of adaptive authentication.
What is Adaptive Authentication?

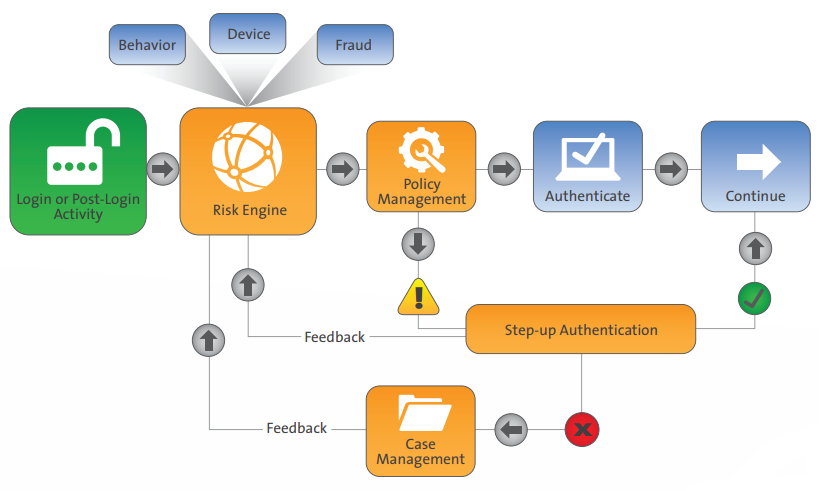
Adaptive authentication is a form of multi-factor authentication wherein it selects only a specific set of authentication factors based on user profiles that depend on several contextual aspects, such as Geo location, proximity to devices, and bio metrics. To achieve this, adaptive authentication deploys an ML (machine learning) algorithm to maintain and dynamically update these authentication factors based on predefined criteria and real time information during each interaction with the user. Such information used may include history of authentication, access failure/success rate, the device used to access, and more.
On a broad level, authentication factors can be categorized into three areas: knowledge-based, location-based, and behavior-based. Knowledge-based factors include methods such as user passwords and pins; location-based factors may include the Geo-location of the user; and behavior-based factors can include using sensors for bio metrics, such as touch id and a retinal scan, and subjective information like patterns of device usage. On the other hand, single factor authentication, although faster, does not provide the highest security.
Adapting to Adaptive Authentication
Many companies are hesitant to adopt adaptive authentication in favor of a fixed security mechanism that provides transparency for monitoring and evaluation. However, these traditional security mechanisms can be exploited when sensitive information is leaked, such as passwords, key pins, and key cards. Adaptive authentication can ensure more reliability as it strategize responses based on an estimated risk derived from user profiles and maintains risk scores from user transactions over time. An entity is deemed risky when abnormalities begin to emerge in authentication; an adaptive authentication model would select the most suitable factors for assessment and can deny access due to these abnormalities. Based on context and requirements, they can be classified as,
Trust-Based Authentication: To overcome the contradiction between privacy and security by enabling trust with selective authentication schemes to prevent sensitive data leakage.
Risk-Based Authentication: To identify the threat before performing evaluation which ensures reliability and effectiveness.
Context-Based Continuous Authentication: Contextual verification of users throughout sessions by monitoring for service usage behavior even after initial authentication.
Industrial Applications
Although there are challenges and uncertainties with theoretical proposals and prototypes, there are companies who are currently implementing adaptive authentication for their products with more adaptive authentication technologies to be released in the near future. As the value for security keeps increasing, organizations are moving towards AI solutions and dynamic security protocols.
Silent Authentication for e-Commerce
The French multinational company Thales, which provides technical services for the aerospace industry, has recently announced a product that uses silent authentication for e-commerce delivery via drones. The company aims to achieve continuous authentication in real time with a seamless experience using the way phones are used, user location, gait (a person’s manner of walking), patterns of actions, and surrounding signals. They aim to achieve,
- Trusted connected objects such as mobile becoming the main form for ID
- Seamless user experience (e.g., if a phone is forgotten at home, there is a temporary device at the office with transferred updated personal phone data)
- Personalized experience (e.g., automatic lighting based on mood)
Adaptive Verification Based on Risk
IBM Security Verify Adaptive Access is a system that helps organizations with secure verification by balancing risk considerations with user experience. A risk calculation engine (IBM Trusteer) developed by IBM is used to assess user profiles throughout digital interactions to provide risk-based policy editor, protect SAAS, analyze threat intelligence, detect suspicious user behavior, assess device hygiene (for malware/viruses) and behavioral bio metric abnormalities.
Benefits
Adaptive authentication leverages three primary concepts:
- Contextual knowledge
- Real-time threat analysis
- Continuous assessment for adaption after authentication
All three notions play a significant role in modern security. With advancements in technology, we now have the means to analyze a variety of data sources through modern sensors along with the computational capability through AI while enabling trust-based security to enhance non-intrusiveness into personal data.
Usability is another aspect to consider in terms of business platforms. User experiences can be improved with personalized accessibility features that do not tire the customers with lengthy authorization protocols while also increasing performance. The environment also plays a key role in determining security processes as certain domains like the medical industry and transportation industry are time sensitive and serious. Finally, continuous monitoring ensures hackers and imposters who may duplicate actual user identities to pass initial authentication, are captured through behavioral analysis during communication with the network.
Opportunities
It is important to note that AI is becoming ever more prominent in computer science and security fields. It is certainly plausible that AI will become incredibly influential in network security as well. From a business perspective, it is becoming more prudent to venture into adaptive authentication technologies as early as possible to gain a market advantage over competitors in strategy and revenue.

Companies already have the physical means and processes that are needed to be brought together to achieve the successful implementation of adaptive authentication techniques. An ISMG (Information Security Media Group) survey in 2019 indicated that adaptive authentication topped the list of authentication investments. The survey also highlighted that only 10% of all financial institutions showed confidence in their security features as 96% of them still use legacy systems. Moreover, 37% percent of these financial institutions have an active initiative that is working towards these technologies. Hence, adaptive authentication is going to be a game changer for organizations needing strong defense to guard customer and enterprise data.
References
https://lpasquale.github.io/papers/ACSOS2021.pdf
https://www.onelogin.com/resource-center/infographics/future-authentication
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/security-verify?topic=access-overview
https://www.ibm.com/products/risk-based-authentication-solution

I was surprised to see the email links were the lowest risk but it seems to make sense as biometrics can be spoofed through images and where someone has went and phones can be stolen, it seems like with a secure password and phishing prevention its logical that emails are the lowest risk. Its very interesting to see that authentication can be dynamic and it seems secure if the ML model is superb, but is the cost to implement such an authentication method similar to a regular authentication model? If not its hard to see an widespread adoption of it even if is secure, I believe that companies will take the larger small risk in their authentication if it saves them big bucks. However, I am interested in seeing the development of adaptive authentication as you mentioned that it topped the list of authentication investment it seems like it could be achievable in the near future.
Adaptive authentication sounds fascinating. I’m not sure I fully understand the exact specifics how it works but the general idea with real time analysis and continuous assessment along with authentication based on user profiles and risk assessment sounds like a great idea if done right and I wouldn’t be surprised if adaptive authentication was the future with how much more prominent AI usage is becoming everywhere.
Very interesting post! Whenever I log into my Gmail or Google Drive at school, a friends house, or a cafe I am always prompted with an authentication request in the form of accessing one of my Google apps on my phone (Typically Youtube and Gmail), then clicking the confirm button. I much rather have this form of authentication compared to getting an email link or a text message and waiting for a code.
Great post, and a really interesting frontier for security technology and practices. By way of a question, you mention in your blog post that some companies are reluctant to implement adaptive security measures, preferring instead the transparency of fixed methods. In your opinion, is there a way to adapt the benefits identified by users of static security methods (i.e. the transparency) and implement it in adaptive methods? Second, you mention that much of these methods are based on the deployment of a machine learning algorithm. In your opinion, is this a source of weakness in the development of these adaptive security measures (such as human error, bias, or compromise), and if so is there a way to account for this weakness?
It is intriguing how you are portraying this. The way I have seen it, AI and machine learning are nowhere near advanced enough to be trusted to do security verification and authentication based on behavioral analysis. Machine Learning AI already have enough trouble understanding the human language, let alone human behavior. Still, this blog post and the cited sources have as much confidence in the AI, perhaps its not as far off as I thought.
With computational power increasing and cyber-crime growing ever more rampant everyday, it’s only natural that we need to improve our authentication systems. The idea of an adaptive system is rather interesting in concept, but I wonder how well this system will work in a practical scenario. I hope these systems will allow people to manually choose their authentication methods as well as I can imagine some people wanting the maximum level of authentication no matter the occasion. Overall an interesting post!
Alright, time to be a debbie downer.
Sure AI/ML based authentication that can automatically authenticate you for delivery purchases or help you sign in sounds great if it could work. But the main concern I have is just the sheer volume of biometric data they can record about you. It seems like an awful lot of biometric and personal data is being recorded and stored on one server, from your gait to your geolocation and frequent stops at specific locations this service seems like it takes a pretty accurate screenshot of your life in order to authenticate you.
Some people may argue that the data is already being collected with fitness apps and other services that record your location, but the main issue I see here is that its all being congregated into one database belonging to one company, which pretty much forms a single point of failure in terms of letting a massive amount of your personal data go.
I personally find no issue with our current methods of authentication, maybe in part to the fact that I’ve been dealing with them for most of my life. It could be that I’m just thinking too hard on this and this system could prove to be very robust and useful to our day to day usage of the internet. But as it stands right now, I believe that the system has a few flaws fundamental to its design that would need to be addressed. This also isn’t to mention people being locked out of their own accounts should some of these factors change, which could prove to be a very arduous process to correct.
All in all, this post was quite enlightening to this topic. I wasn’t aware of this system before reading. Thanks for the post!
Interesting post! Before coming to this course I was always a little annoyed whenever multifactor authentication came up but after learning the importance I do agree with you that one time authentication is not secure. However I am not so sure that this is the way either. I’m not sure if I didn’t quite understand the concept but from what i am grasping there will be a risk machine trying tot figure out if authentication is needed but I don’t see how this is necessarily better then the systems we have now. Plus with the added recording of personal data which would be from a vast majority of different organizations if implemented, I’d really rather prefer taking a couple more second to do the multifactor authentication we have now.
Interesting post. Although adaptive authentication is a new technology, this new security mechanism can ensure higher reliability than the traditional one. The article mentioned that this new technology has continuous authentication based on trust, risk and context, which enhances security and non-invasiveness to personal data. This will bring strong defence to the data of customers and companies. However, adaptive authentication updates authentication factors according to the ML algorithm, which makes it difficult to doubt whether this algorithm is absolutely accurate. However, with the continuous development of security technology, I think adaptive authentication technology will continue to improve its functions to ensure the data security of customers.
Very Informative post! While I can clearly see the benefits of adaptive authentication, I just feel like it might be very difficult to implement because of all the factors that come into play, and so that is why companies aren’t really making use of it. But once this initial obstacle is scaled, then I think this would be the future of authentication.
Interesting and informative post! I was not familiar to the the terminology adaptive authentication, but after reading the post, I realize I might have been using something similar. When login to my Instagram, Google or Microsoft accounts on new devices, I always receive warning emails, and multiple factors of authentication. For example, an interesting authentication I experienced recently was when I tried to login to Google on a new device, I was asked to open a specific app, YouTube or Google Drive, to authenticate the login. I find this process secure as no message was given to my phone unless I perform the required action. Overall, I find the use of AI for adaptive authentication brilliant and would love to see more creative and secure authentication with adaptive authentication.
Great post! I think that it’s great that newer technologies such as AI are being used in cybersecurity. However, I do think that due to the very fast past of this industry, it’s going to be very difficult to gather an up-to-date dataset to perform machine learning on. And that isn’t saying anything about the quality of that data. Another problem I see would be the lack of privacy. This adaptive authentication seems very intrusive.
Great post. It is very interesting that AI is starting to be implemented in cyber security. I think this is a very good thing because, with the use of AI, cybersecurity can be strengthened a lot.
I can see tons of use cases here that will get rid of/render absolute the use of physical IDs, not just government issued ones-but also work related authentication.
This was a really good post! AI usage is becoming more and more prevalent in our technological age. Even though, I do not have complete faith that AI can handle the authentication and verification work (since I do no think AI can fully understand human behaviour yet), I do think the new age will go towards that direction. Moreover, I never actually believed in one-time authentication since it never really felt secure. I believe multi-factor authentication is more secure and even though it can be a hassle to deal with it everytime, it is better than someone else invading your privacy. I even heard of hackers who got through the multi-factor authentication of another user, so even that may not suffice sometimes.
Email does seem to be quite secure in how especially google notifies me right away if I login anywhere besides my home! Also I guess this could be a testament to humans getting smarter with defending against phishing?